5.2 KiB
| title | slug | date | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waybar customisation | /waybar-customisation/ | 2024-03-03 |
|
On my local machine I am currently replacing my desktop environment (Gnome) with a tile-based window manager (Hyprland). I'm trying to strip out the bloat and have a lightweight and highly customised Arch workhorse.
A key component is a useful status bar that displays metrics and provides a means of quickly executing common tasks. Previously, when I was using X, I opted for Polybar but now that I am on Wayland I'm using waybar. So far, I've added two custom modules: one for displaying code metrics and another for managing my time-tracking.
Code metrics module
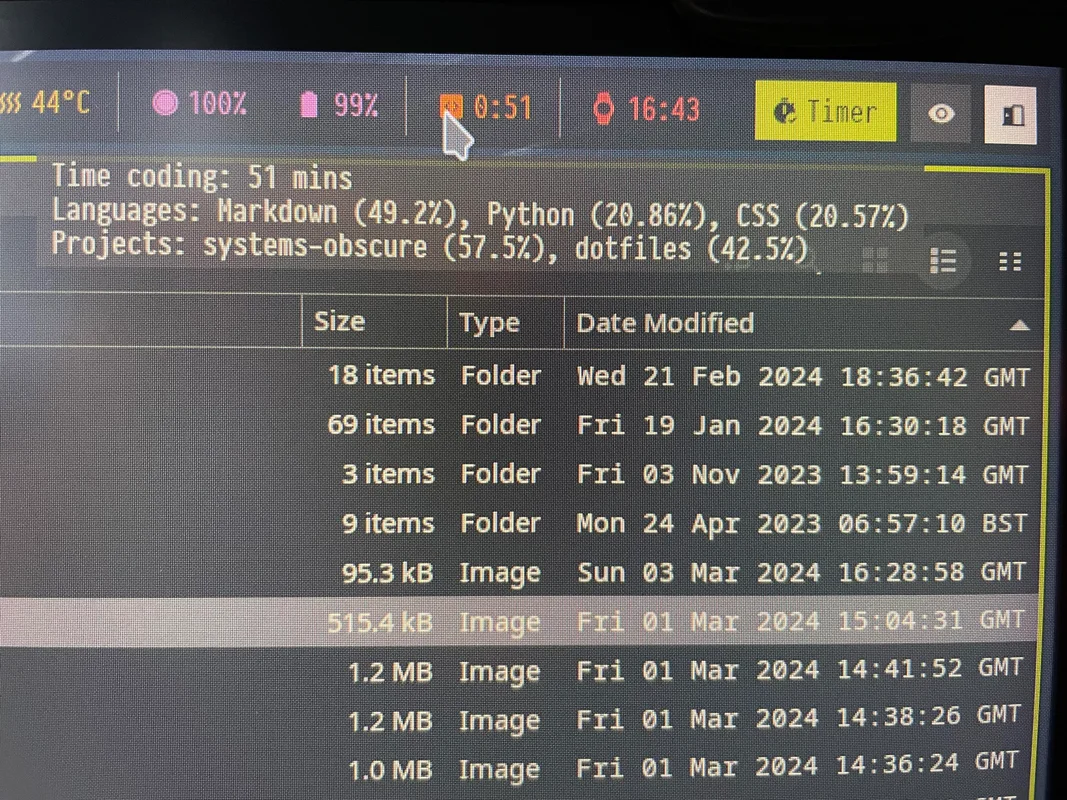
I use WakaTime to collate metrics on my coding activity (time coding, programming languages, projects etc.) I already have a dashboard on this site that displays some of this data but I thought it would be useful to see my stats from the status bar as I am working.
Below is an image of the module. The permanent display outputs the coding duration for the current day. When you hover you see a summary of the main languages used and the main projects I've been working on.
It's a straightforward Python script that queries the WakaTime API and parses the data and forwards it to the module:
#! /usr/local/bin/python3
import requests
import os
import json
import textwrap
WAKATIME_API_KEY = os.getenv("WAKATIME_API_KEY")
WAKATIME_ENDPOINT = "https://wakatime.com/api/v1/users/current/status_bar/today"
def get_data(url):
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
return response.json()
else:
raise Exception(
f"Failed to fetch data from API. Status code: {response.status_code}"
)
def generate_tooltip(time, languages, projects):
return textwrap.dedent(
f"""\
Time coding: {time}
Languages: {languages}
Projects: {projects}"""
)
def format_metric(metrics):
return ", ".join(
[f'{metric["name"]} ({metric["percent"]}%)' for metric in metrics[:3]]
)
def main():
output = {}
try:
data = get_data(WAKATIME_ENDPOINT + "?api_key=" + WAKATIME_API_KEY)
digital_time = data["data"]["grand_total"]["digital"]
human_time = data["data"]["grand_total"]["text"]
langs = data["data"]["languages"]
projects = data["data"]["projects"]
tooltip = generate_tooltip(
human_time, format_metric(langs), format_metric(projects)
)
output["text"] = digital_time
output["tooltip"] = tooltip
except Exception as e:
output["text"] = "Error"
print(json.dumps(output))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Here's the module declaration in the Waybar config:
"custom/wakatime": {
"exec": "source $HOME/dotfiles/.env && python3 $HOME/.config/waybar/resources/custom_modules/wakatime_waybar.py",
"format": " {}",
"return-type": "json",
"interval": 600
},
Time-tracking module
I've recently started using time warrior to track my extra-curricular coding and study. This is a command-line time-tracker so it integrates really well with Waybar.
The module highlights green when there is an active timer. This helps to remind me to stop the timer! When you click the current timer stops and when you right-click it resumes. This saves me going into the terminal when I stopping and starting an ongoing piece of work.
Again I've used Python for the scripting:
#! /usr/local/bin/python3
import subprocess
import json
def invoke_shell(proc):
try:
result = subprocess.run(
proc,
shell=True,
check=True,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
text=True,
)
return result.stdout.strip()
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
return e.stderr.strip()
def timer_active() -> bool:
status = invoke_shell("timew get dom.active")
if status == "1":
return True
else:
return False
def generate_tooltip():
tooltip = invoke_shell("timew summary :week")
return tooltip
def main():
output = {}
try:
if timer_active():
output["text"] = " Timer"
output["class"] = "active"
else:
output["text"] = " Timer"
output["class"] = "inactive"
except Exception as e:
output["text"] = "Error"
print(json.dumps(output))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
And here is the module declaration in the Waybar config:
"custom/timewarrior": {
"exec": "python3 $HOME/.config/waybar/resources/custom_modules/time_warrior_waybar.py",
"format": "{}",
"on-click": "timew stop && notify-send 'Time Warrior' 'Timer stopped'",
"on-click-right": "timew continue && notify-send 'Time Warrior' 'Timer resumed'",
"return-type": "json",
"interval": 5
},